Create Calculated Fields in Microsoft Access Select Queries
by Avantix Learning Team | Updated October 14, 2022
Applies to: Microsoft® Access® 2010, 2013, 2016, 2019, 2022 and 365 (Windows)
You can create calculated fields in select queries in Microsoft Access in the QBE (query by example) grid. You'll need to learn a few syntax rules and then you can create simple to more complex calculations. Calculated fields can also be created in other types of Access queries.
Recommended article: 10 Microsoft Access Tips for Working with Select Queries
Create a calculated field in a select query
To create a select query with a calculated field (which would appear in each record in Datasheet View):
- Click the Create tab in the Ribbon and then click Query Design in the Queries group.
- Double-click the desired tables and then click Close.
- In the grid, in a blank column in the Field row, enter the new field name followed by a colon (:). Anything after the colon is part of the mathematical expression used in the field. When you enter the name of the new field, do not use periods (.), square brackets ([]) or exclamation marks (!). Also, do not use the same name as another field in a table in your database.
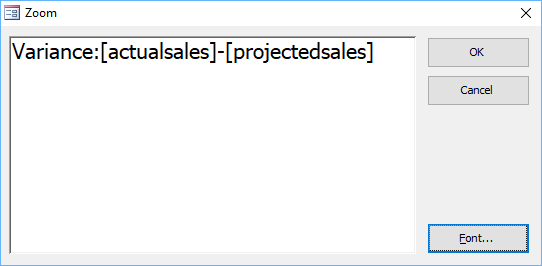
- After the new field name and the colon, enter the expression. When you enter field names in the expression, they should appear in square brackets such as [actualsales]. You can right-click in the field row and select Zoom or press Shift + F2 to "zoom in" to make it easier to enter the expression. For example, you could enter Variance:[actualsales]-[projectedsales] in the field row or Zoom dialog box.
- In the expression, enter any operators or functions as appropriate (+ for addition, – for subtraction, / for divide and * for multiply). You can also enter Access functions.
- If you are in the Zoom dialog box, click OK.
- Press Enter.
- Right-click the tab for the query and select Datasheet View. You can also click Run in the Results group in the Query Tools Design tab in the Ribbon.
In order for these calculations to work, the fields that you include in the expression should be fields in the displayed tables. Also, watch out for typing errors. Actual Sales is different from ActualSales and square brackets, not round brackets, are used to enclose the fields.
Below is the Zoom dialog box:
A calculated field in Design View in a query may appear in the Field row as follows:
Variance:[ActualSales]-[ProjectedSales]
These calculations are not case sensitive so you could also enter:
Variance:[actualsales]-[projectedsales]
Create a calculated field using the Expression Builder
To create a query with a calculated field using the Expression Builder:
- In Query Design View, in the grid, click in a blank column in the Field row and then enter the new field name followed by a colon (:).
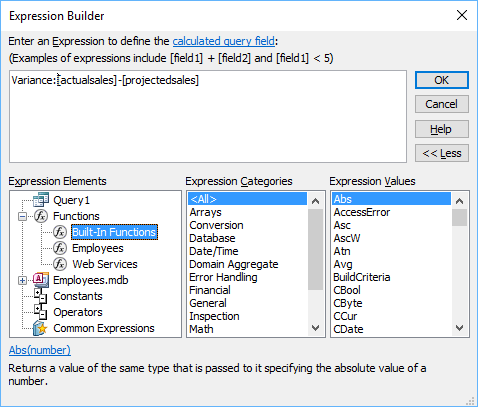
- Click Builder in the Query Setup group in the Query Tools Design tab in the Ribbon or press Ctrl + F2. The Expression Builder appears. Enter the expression or click the + beside Functions and then click Built-In Functions to view the functions available in Access.
- Continue entering the desired formula.
- Click OK.
- Press Enter.
- Right-click the tab for the query and select Datasheet View. You can also click Run in the Results Area in the Query Tools Design tab in the Ribbon.
Below is the Expression Builder:
You can create all kinds of basic and more complex calculations using the functions in Microsoft Access not only in queries, but in forms, reports and other objects. We'll be showing some of the other calculations you can create in future articles.
Subscribe to get more articles like this one
Did you find this article helpful? If you would like to receive new articles, JOIN our email list.
More resources
Key Features and Benefits of Microsoft Access
How to Filter a Report on the Fly in Microsoft Access
10 Tips for Creating Select Queries in Microsoft Access
10 Techniques for Designing Forms in Microsoft Access
How to Convert a Microsoft Access Report to PDF (3 Ways)
Related courses
Microsoft Access: Introduction
Microsoft Access: Intermediate / Advanced
Microsoft Access: Introduction to VBA (Visual Basic for Applications)
Our instructor-led courses are delivered in virtual classroom format or at our downtown Toronto location at 18 King Street East, Suite 1400, Toronto, Ontario, Canada (some in-person classroom courses may also be delivered at an alternate downtown Toronto location). Contact us at info@avantixlearning.ca if you'd like to arrange custom instructor-led virtual classroom or onsite training on a date that's convenient for you.
Copyright 2024 Avantix® Learning
You may also like
How to Replace Zeros (0) with Blanks in Excel
There are several strategies to replace zero values (0) with blanks in Excel. If you want to replace zero values in cells with blanks, you can use the Replace command or write a formula to return blanks. However, if you simply want to display blanks instead of zeros, you have two formatting options – create a custom number format or a conditional format.
What is Power Query in Excel?
Power Query in Excel is a powerful data transformation tool that allows you to import data from many different sources and then extract, clean, and transform the data. You will then be able to load the data into Excel or Power BI and perform further data analysis. With Power Query (also known as Get & Transform), you can set up a query once and then refresh it when new data is added. Power Query can import and clean millions of rows of data.
How to Freeze Rows in Excel (One or Multiple Rows)
You can freeze one or more rows in an Excel worksheet using the Freeze Panes command. If you freeze rows containing headings, the headings will appear when you scroll down. You can freeze columns as well so when you scroll to the right columns will be frozen.
Microsoft, the Microsoft logo, Microsoft Office and related Microsoft applications and logos are registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation in Canada, US and other countries. All other trademarks are the property of the registered owners.
Avantix Learning |18 King Street East, Suite 1400, Toronto, Ontario, Canada M5C 1C4 | Contact us at info@avantixlearning.ca